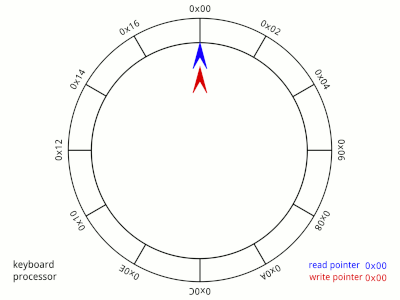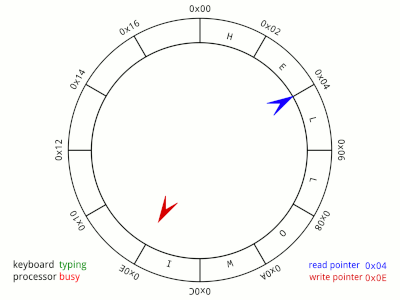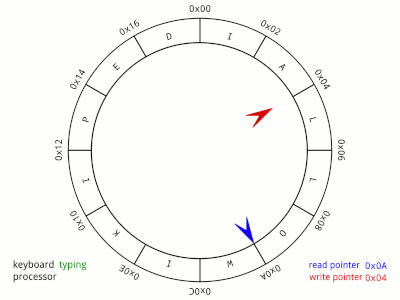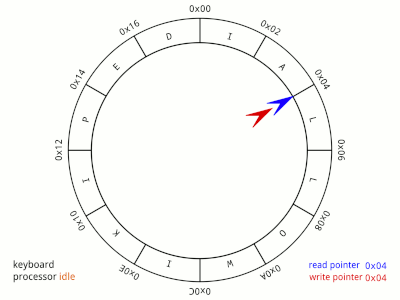
A circular queue is an extended version of a regular queue. Unlike a linear queue, the last element of a circular queue connects back to the first element, forming a circular structure. This is useful for efficiently managing fixed-size data buffers.
Advantages of Circular Queues
- Efficient Space Utilization: The circular nature allows reusing spaces once occupied by dequeued elements, avoiding the "overflow" issue common in linear queues.
- Fixed Size Management: Ideal for scenarios where the size is fixed and limited, such as buffering in hardware systems.
Disadvantages
- Complexity: Managing the front and rear pointers requires careful consideration, especially in detecting when the queue is full or empty.
- Limited Capacity: Once the queue is full, additional enqueues cannot happen until space is freed.
Time Complexity Analysis
Let \(n\) represent the number of elements in the queue:
- Enqueue: \(O(1)\)
- Dequeue: \(O(1)\)
- Peek/Front: \(O(1)\)
- Check if Full or Empty: \(O(1)\)
Circular Queue Implementation Using an Array in C++
Header Implementation
Implementation Details
Example Usage
Conclusion
A circular queue efficiently handles fixed-size buffers with constant time complexity for both enqueue and dequeue operations. It is particularly useful in applications like round-robin scheduling and data buffering where limited, cyclic memory management is crucial.